Good Manufacturing Practice standards protect consumers from contamination, ensure product consistency, and support regulatory compliance. For toothpaste manufacturers, GMP-compliant equipment represents both a quality requirement and competitive advantage.
Recent enforcement actions highlight GMP’s importance. In November 2024, the FDA issued a warning letter to Tom’s of Maine after discovering bacteria contamination including Pseudomonas aeruginosa in water used for toothpaste production.
Multiple recalls followed, with over 4.6 million toothpaste products recalled in 2025 for Current Good Manufacturing Practice (CGMP) deviations. This guide explains how GMP standards apply to toothpaste filling and packaging equipment, detailing design principles, material requirements, and process controls that support safe, compliant manufacturing.
What Is GMP and Why It Matters in Toothpaste Manufacturing
Good Manufacturing Practice establishes systematic approaches to production, quality control, and documentation. These practices minimize contamination risks and production errors affecting product safety.
ISO 22716:2007 provides international GMP guidelines for cosmetics, including oral care products. In 2007, the International Cooperation on Cosmetic Regulations (ICCR)—comprising the United States, Canada, European Union, and Japan—agreed that ISO 22716 would serve as the foundation for cosmetic GMP standards.
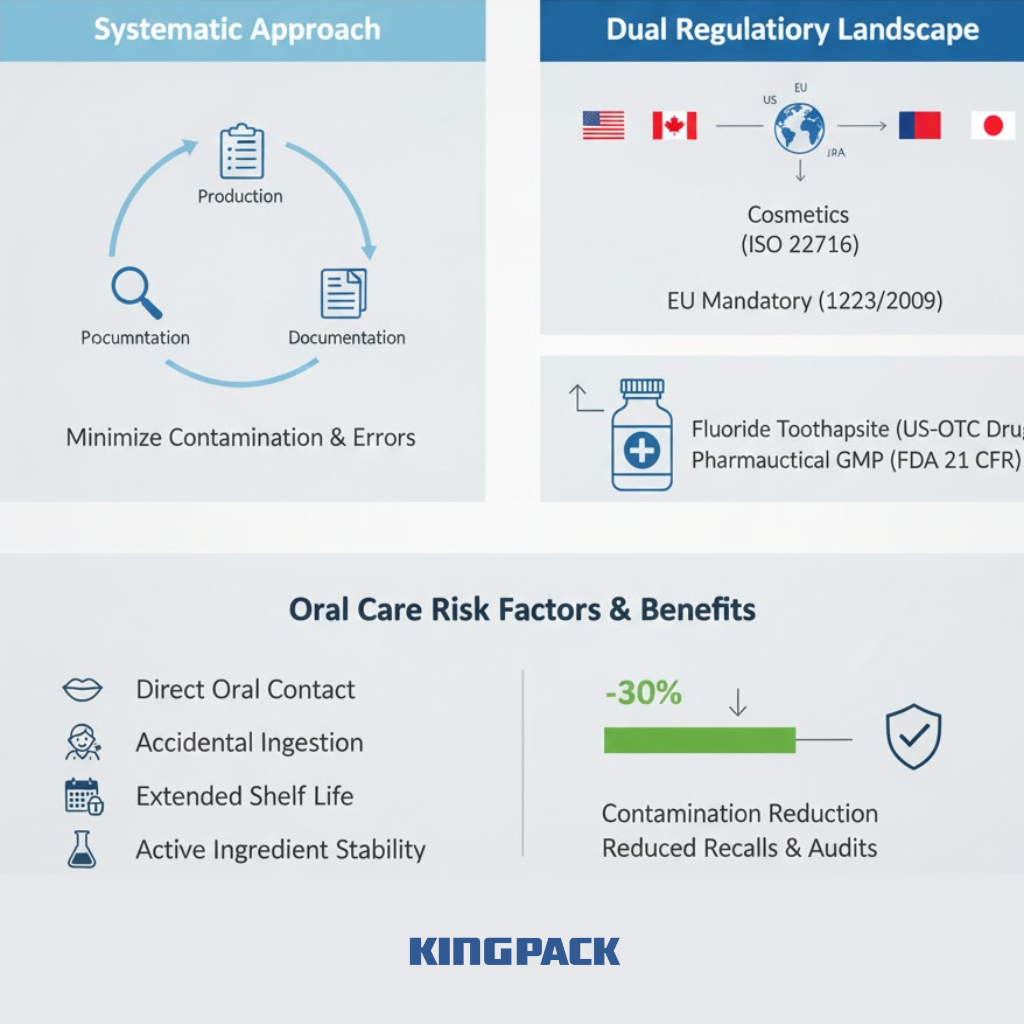
Toothpaste occupies a unique regulatory position. Standard formulations classify as cosmetics in most markets. Fluoride toothpaste qualifies as an over-the-counter (OTC) drug in the United States, requiring compliance with pharmaceutical GMP regulations (FDA 21 CFR 210 and 211).
The European Union’s Cosmetics Regulation 1223/2009 mandates that all cosmetic products, including toothpaste, must be manufactured according to Good Manufacturing Practices based on ISO 22716. This requirement makes GMP compliance mandatory rather than optional for EU market access.
GMP Requirements for Toothpaste Filling and Packaging Equipment
Equipment design directly impacts manufacturing quality and contamination prevention capabilities.
Hygienic Equipment Design

Sanitary design principles prevent product contamination and facilitate effective cleaning. Key requirements include:
- Smooth, crevice-free surfaces that eliminate locations where product residue accumulates
- No dead corners or blind spots that prevent product stagnation and bacterial growth
- Easy disassembly for inspection using tri-clamp connections for tool-free maintenance
- Rounded edges and corners throughout construction to prevent product entrapment
- Sloped surfaces that provide complete drainage paths
- Accessible design supporting both automated and manual cleaning verification
Recommended Reading: Top 10 Tube Filling Machine Manufacturers Today – Global Leaders in Tube Packaging Technology – King Pack Machinery
Material Compliance
Product-contact materials must meet food-grade and pharmaceutical standards depending on toothpaste classification.
| Material Type | Standard Grade | Application | Key Properties |
| Stainless Steel | 316L | Product-contact surfaces | Superior corrosion resistance, low-carbon |
| Seals & Gaskets | FDA-approved silicone, EPDM, FKM | All sealing points | Chemical resistant, temperature tolerant |
| Plastic Components | PTFE, UHMW-PE, food-grade PP | Non-metallic parts | FDA-compliant, cleanable |
| Welding Materials | 316L filler rod | Joints and connections | Matches base material properties |
Material certification documentation accompanies GMP-compliant equipment. King Pack provides complete material traceability demonstrating regulatory compliance.
Cleanability and Sanitization
Effective cleaning removes product residue and microbiological contamination between production batches.
Clean-In-Place (CIP) systems include:
- Spray balls and spray nozzles for complete coverage
- Automated alkaline wash cycles (60-70°C)
- Intermediate rinses removing chemical residue
- Acid wash cycles (50-60°C) for mineral deposit removal
- Final purified water rinses
- Conductivity sensors verifying rinse completeness
CIP systems reduce cleaning time from hours to minutes compared to manual methods. They also improve cleaning consistency by eliminating operator variation.
Recommended Reading: How to Manufacture Toothpaste: The Role of Filling & Sealing Machines in Production – King Pack Machinery
GMP-Compliant Filling Systems for Toothpaste
Filling accuracy and contamination prevention represent critical GMP concerns during primary packaging.
Accurate and Consistent Filling
Dose accuracy affects both regulatory compliance and product quality. Under-filled tubes violate weight declarations. Over-filling wastes product and reduces profitability.
Filling technology comparison:
| Technology | Accuracy | Best Application | GMP Advantage |
| Servo-driven systems | ±1% | All viscosities | Closed-loop control, data logging |
| Piston filling | ±1-2% | High-viscosity pastes | Positive displacement, repeatable |
| Pump filling | ±2% | Medium viscosity | Gentle handling, continuous flow |
Batch consistency tracking requires documentation proving filling consistency within and between batches. Automated data logging captures every fill weight. Statistical process control identifies variations requiring investigation.
Closed and Controlled Filling Environment
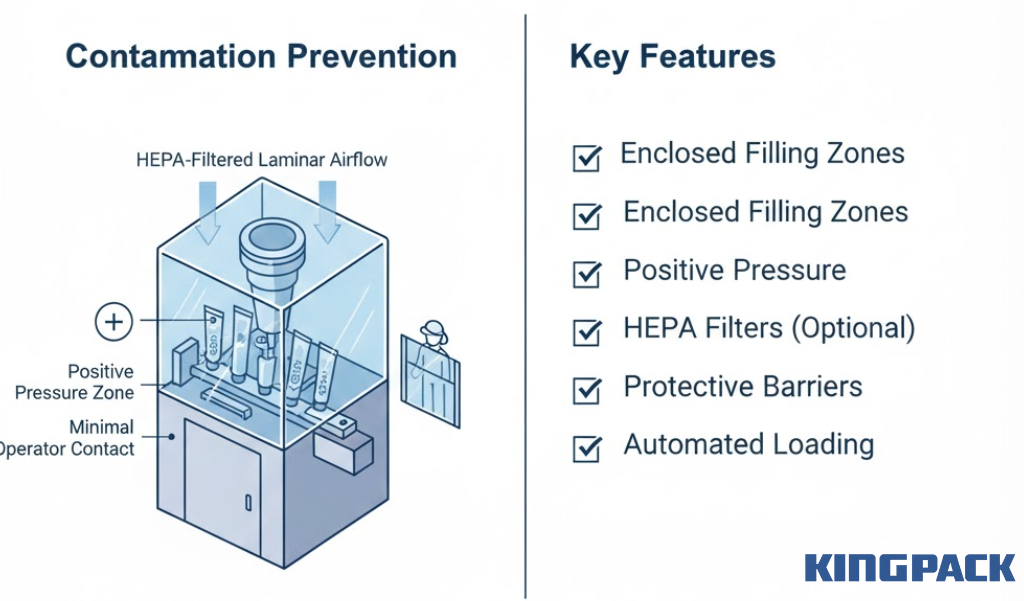
Environmental controls prevent airborne contamination during filling operations.
Protection measures include:
- Enclosed filling zones isolating product from ambient air
- Positive pressure maintenance relative to surrounding areas
- Optional HEPA-filtered laminar airflow systems
- Protective barriers minimizing operator contact
- Automated loading reducing manual product handling
King Pack designs toothpaste filling equipment with GMP-oriented features including enclosed filling zones, servo-driven accuracy, and sanitary construction throughout product paths.
GMP Standards for Tube Sealing and Packaging
Post-filling operations require continued contamination protection and quality control.
Hygienic Tube Sealing Technology
Sealing creates protective barriers preventing contamination after filling.
Material-specific sealing requirements:
- Aluminum tubes: Folding dies and crimping tools require regular cleaning inspection
- Laminated tubes: Hot air systems (160-220°C) generate clean seals without external contact
- Ultrasonic sealing: High-frequency vibration (20-40 kHz) creates contamination-free bonds
- Post-seal handling: Sealed tubes discharge directly to clean conveyors and cartons
Code Printing and Traceability
Batch identification supports product tracking and recall management.
GMP traceability requirements:
- Unique batch numbers on every package
- Manufacturing and expiration dates clearly printed
- Vision systems verifying code presence and legibility
- Automatic rejection of improperly marked products
- Data integration with production records
Automation and Process Control Under GMP
Automated systems reduce contamination risks while improving consistency and documentation.
Reduced Human Intervention
Manual operations introduce contamination variables that automation eliminates.
Automation benefits:
- Minimal human contact transferring microorganisms
- Repeatable operations eliminating operator variation
- Consistent performance across shifts and personnel
- Reduced training requirements and human error
- Batch-to-batch quality uniformity
PLC and HMI Control Systems
Programmable logic controllers coordinate equipment operations and document production parameters.
Control system capabilities:
| Feature | Function | GMP Benefit |
| Recipe management | Stores formulation-specific settings | Prevents setup errors during changeovers |
| Parameter recording | Logs fill weights, temperatures, cycle times | Demonstrates process control for audits |
| Alarm systems | Alerts for deviations and malfunctions | Enables immediate corrective action |
| Audit trails | Automatic documentation of all operations | Satisfies regulatory documentation requirements |
GMP Design Considerations Across the Entire Toothpaste Line
Complete production lines require integrated GMP compliance from raw materials through finished packaging.
Mixing, Filling, and Packaging Integration
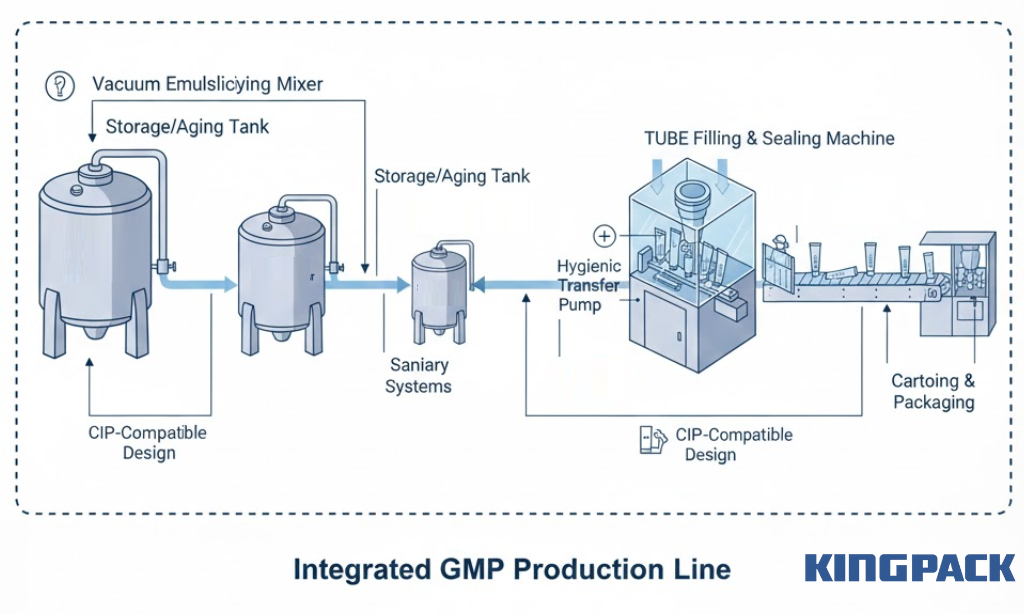
Material transfer between processes demands contamination prevention.
Toothpaste manufacturing flows from vacuum emulsifying mixing through aging tanks to tube filling and finally cartoning. Each transfer point represents potential contamination risk.
Integrated line GMP features:
- Closed transfer systems using sanitary pipelines
- Vacuum transfers eliminating environmental exposure
- Tri-clamp fittings at all connection points
- Hygienic transfer pumps (lobe or progressive cavity types)
- CIP-compatible design across all equipment
King Pack provides integrated production line solutions coordinating mixing, storage, filling, and packaging equipment. This system-level approach guarantees compatible GMP design across all processing stages.
Layout and Workflow Compliance
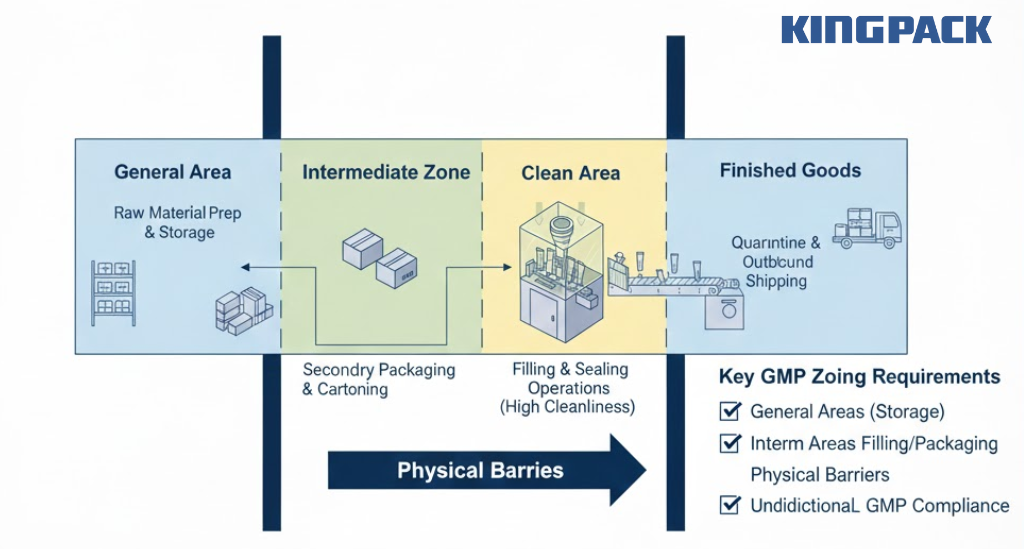
Facility design supports GMP through proper space allocation and material flow.
Zoning requirements:
- General areas: Raw material preparation and storage
- Clean areas: Filling and sealing operations (higher cleanliness standards)
- Intermediate zones: Secondary packaging and cartoning
- Physical barriers: Separation preventing cross-contamination
- Unidirectional flow: Materials progress from lower to higher cleanliness areas
Common GMP Challenges in Toothpaste Equipment
Understanding recurring GMP issues helps manufacturers choose the right Packaging Machines and set procedures that hold up under inspection. This applies across industry application areas, including personal care and cosmetics.
Difficult-to-Clean Machine Design
Poor cleanability remains a core GMP risk. Complex machine layouts, narrow product paths, and hidden cavities trap residue from viscous and pasty materials such as toothpaste. These issues often appear around the filling nozzle, stainless steel butterfly valve, or internal transfer points.
A compliant Toothpaste Filling and Sealing Machine uses smooth stainless surfaces, short flow paths, and accessible parts. Designs inspired by hygienic systems used in Glass Bioreactor or Bioreactor Fermenter setups show how simplified geometry reduces contamination risk. Clean-in-place concepts seen in Fermentation separation equipment, Tubular Centrifuge, and ceramic membrane separation systems offer useful benchmarks.
Cross-Contamination Between Batches
Inadequate cleaning between formulations causes carryover. Flavor residue affects taste. Active ingredients raise safety concerns, especially when switching products within a Plastic Toothpaste Tube or aluminum tube filling line.
Validated cleaning protocols are essential. Equipment must allow sampling and inspection after wash cycles. Systems with quick-release Machinery Accessories and easy access to the control mechanism support verification. Similar validation logic applies in disc centrifuge, Decanter Centrifuge Separator, and spray dryer operations used in pharmaceutical and food processing.
Inconsistent Filling and Sealing Performance
Unstable output signals control issues. Fill weight variation, weak tube seals, or uneven sealing and printing usually trace back to poor calibration or outdated drives.
Modern solutions rely on servo systems aligned with GMP dosing pump standards. A Fully Automatic Filling Sealing Machine with closed-loop feedback keeps output within the defined filling range.
Operators can modify the frequency through a full-color touch screen or touch screen control panel, improving control during format changes. Features like auto tube feed, photoelectric inductance, and an integrated safety device further stabilize production.
Inspection and Documentation Gaps
Equipment failures during audits often come from paperwork, not mechanics. Missing material certificates, weak validation files, or incomplete change records lead to findings.
GMP-ready suppliers provide full documentation packages. IQ, OQ, and PQ protocols prepare machines for inspection. This approach mirrors compliance practices used with Soft Gelatin Capsules Machines, Suppository Filling Machine, and broader Suppository Production Equipment lines.
Broader Equipment Context
While toothpaste production focuses on tube filling, GMP expectations align with other regulated machinery, from Coffee Capsule Filling and Sealing Machine systems to processing equipment handling sealants and adhesives. Lessons from fermentation, separation, and dosing technologies translate directly into more reliable toothpaste manufacturing.
How King Pack Designs GMP-Oriented Toothpaste Equipment
King Pack incorporates GMP principles throughout equipment design and manufacturing.
Hygienic Mechanical Design Philosophy
All product-contact surfaces feature smooth electropolished finishes. Welded joints receive special attention—grinding and polishing match surrounding surface quality. These finishing steps eliminate contamination harboring locations.
Dead zones receive elimination through design optimization. Sloped surfaces and complete drainability prevent product accumulation. Internal corners use generous radii facilitating cleaning access.
Equipment disassembly uses sanitary tri-clamp connections. Operators remove product-contact components without tools. This accessibility supports thorough inspection and verification.
GMP-Friendly Tube Filling and Sealing Machines
King Pack tube filling and sealing machines accommodate both aluminum and plastic laminated tubes with quick-change capability. Dual-purpose design provides flexibility while maintaining GMP compliance across materials.
Enclosed filling zones protect product during dispensing. Servo-driven dose control maintains filling accuracy within ±1% specifications. CIP-compatible design supports automated cleaning between production batches.
Sealing systems integrate temperature controls and cooling stations. Consistent seal quality results from precise parameter management. Vision systems verify seal integrity automatically.
Flexible Configuration for Different GMP Levels
Cosmetic-grade toothpaste requires ISO 22716 compliance. Fluoride toothpaste classified as OTC drugs needs pharmaceutical-grade GMP meeting FDA 21 CFR 210/211.
King Pack engineers equipment configurations matching specific market requirements. Basic cosmetic GMP systems provide essential sanitary design and documentation.
Pharmaceutical-grade configurations add enhanced controls, validation packages, and regulatory support documentation.
This flexibility allows manufacturers to specify appropriate GMP levels without over-engineering or compromising compliance.
When GMP-Compliant Equipment Becomes a Business Advantage
Beyond regulatory necessity, GMP compliance creates competitive benefits.
Easier Market Access and Export Approval
Many countries require GMP compliance for imported toothpaste. The European Union mandates cosmetic GMP compliance. Middle Eastern markets increasingly enforce GMP requirements.
Equipment providing GMP documentation facilitates market access approvals. Regulatory submissions include equipment specifications and validation records. Pre-qualified equipment accelerates approval timelines.
Faster Customer and Regulatory Audits
Contract manufacturers serving major brands face frequent customer audits. Brand owners verify supplier compliance before approving production.
GMP-compliant facilities complete audits efficiently. Organized documentation, validated cleaning procedures, and properly designed equipment satisfy auditor requirements. Smooth audits support ongoing business relationships.
Regulatory inspections occur with varying frequency depending on jurisdiction and product classification. Facilities demonstrating consistent GMP compliance receive favorable inspection outcomes.
Improved Brand Trust and Product Quality
Consumers increasingly value manufacturing quality and safety standards. Brand reputation suffers when recalls occur due to contamination or quality failures.
A retrospective regulatory analysis of FDA recalls from 2012 to 2023 revealed that inadequate compliance with current Good Manufacturing Practices represents one of the most frequent recall causes.
The study identified five primary cGMP violation types: process control issues, inadequate storage practices, manufacturing problems, impurity presence, and stability concerns.
GMP compliance prevents these failures. Consistent manufacturing processes produce uniform product quality. Contamination prevention protects consumer health and brand reputation.
Long-Term Risk Reduction
Recalls create substantial costs beyond direct product replacement. Investigation expenses, regulatory penalties, legal liabilities, and brand damage multiply financial impact.
The Tom’s of Maine case illustrates consequences. Following the 2024 FDA warning about bacterial contamination in manufacturing water, the company faced facility improvements, process changes, and reputation damage requiring extensive remediation.
Investing in GMP-compliant equipment prevents these scenarios. While initial costs exceed basic equipment, long-term risk reduction justifies the investment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is toothpaste production required to follow GMP?
Yes. EU follows ISO 22716, US fluoride toothpaste follows 21 CFR 210/211, and MoCRA will mandate GMP for all cosmetics in the US.
What GMP features should a toothpaste filling machine have?
316L stainless steel, sanitary fittings, enclosed filling, servo dosing, CIP cleaning, and full documentation. King Pack includes these by default.
How does GMP affect tube sealing technology?
Seals must prevent contamination. Aluminum uses folding/crimping; laminated uses controlled heating. Calibration ensures consistent quality.
Can one line meet different GMP standards?
Yes. King Pack lines can meet cosmetic or pharmaceutical GMP through flexible design and documentation.
Does GMP equipment support future expansion?
Yes. Modular designs allow adding lines or upgrading mixers without replacing the system.
Conclusion
GMP compliance is essential for safe, high-quality toothpaste manufacturing. King Pack’s equipment combines sanitary design, robust materials, and flexible documentation to meet global regulatory standards while supporting future expansion.
Contact King Pack today to implement GMP-compliant toothpaste production systems, optimize efficiency, and ensure consistent product quality.

