Modern toothpaste production requires precision at every stage. From raw material mixing to final packaging, manufacturers face technical challenges that directly impact product quality, production efficiency, and profitability.
Understanding these challenges and implementing the right solutions separates successful operations from struggling facilities. This guide examines the five most critical obstacles in toothpaste manufacturing and demonstrates how integrated production lines address each issue.
Why Toothpaste Manufacturing Is More Complex Than It Looks
Toothpaste appears simple but its production demands exacting control over multiple variables. The paste must maintain consistent viscosity across thousands of tubes. Active ingredients like fluoride require precise distribution to meet regulatory standards.
Temperature fluctuations during mixing affect ingredient stability. Air incorporation creates texture problems and reduces shelf life. Contamination risks threaten both product safety and regulatory compliance. These challenges multiply across different formulations—whitening pastes behave differently than sensitivity formulas.
According to recent industry reports, facilities with GMP certification achieve contamination rate reductions of up to 30%. This statistic highlights how proper equipment and processes directly impact production outcomes. King Pack’s integrated toothpaste production lines address these complexities through coordinated equipment design and automation.
Recommended Reading: Top 10 Tube Filling Machine Manufacturers Today – Global Leaders in Tube Packaging Technology – King Pack Machinery
Challenge 1 – Inconsistent Mixing and Unstable Formulations
Uneven mixing creates serious quality problems. Ingredients separate, sodium fluoride spreads unevenly, and abrasives settle or form lumps. The paste feels gritty, taste shifts from batch to batch, and defects become visible inside the toothpaste tube. These issues affect oral care products across many segments, from children’s toothpaste to SLS Free Toothpaste and tooth whitening lines.
Common Causes:

- Low shear forces: An industrial mixer without enough shear cannot disperse hydrated powders and rheology modifiers, which leads to clumping and poor texture.
- Incorrect ingredient sequence: Adding thickeners before the Liquid Base traps dry pockets and disrupts the toothpaste formula.
- Short mixing time: Rushed Processing methods stop the system from forming a true homogeneous mixture.
- Poor temperature control: Ingredients such as humectants, Flavoring oils, and Sodium saccharinate react differently at unstable temperatures, which affects consistency and taste.
These problems appear often in private label production, where multiple toothpaste formulations run through the same production unit.
Solution: Integrated Vacuum Mixing System
King Pack addresses these issues with vacuum emulsifying systems designed for modern Toothpaste Manufacturing Equipment. The setup combines controlled shear, vacuum, and temperature management to stabilize dental products at scale.
- High-shear mixing: A Rotor/stator assembly inside a homogenizer mixer operates at high speed to refine particles and support smooth dispersion across varied ingredient selection needs.
- Vacuum processing: Removing trapped air helps stabilize texture and protects sensitive components used in oral hygiene products.
- Precise temperature control: Jacketed vessels support heating and cooling stages required for stable emulsions and repeatable viscosity testing.
- Controlled ingredient addition: Multiple feed points allow accurate dosing during production technology workflows, reducing operator variation.
This setup supports consistent quality across Custom Private Label Formulations, including Private Label Mouthwash and toothpaste tablets.
Challenge 2 – Air Bubbles and Product Defoaming Issues
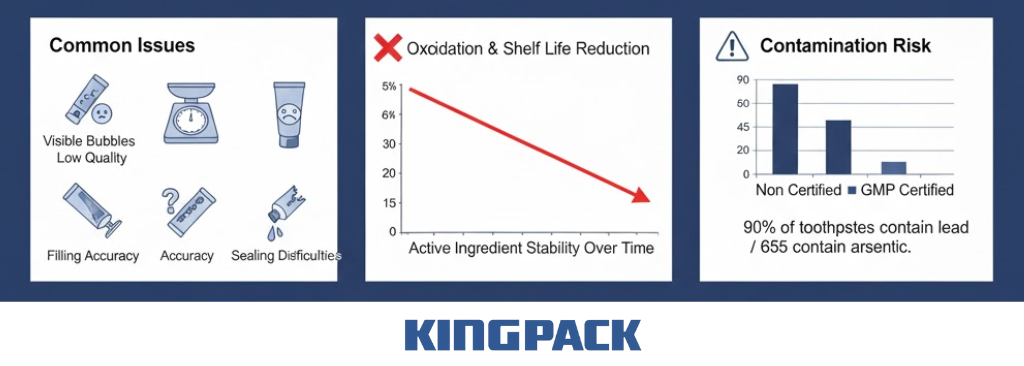
Air trapped during mixing leads to visual flaws and functional failures. Bubbles reduce shelf appeal and weaken sealing at the toothpaste tube stage. These issues create problems during filling, transport, and storage, especially for private label manufacturer operations handling large volumes.
Why Air Entrapment Is a Serious Problem
Air enters the paste at several points. High-speed blending in an In-Line mixer pulls in air. Transfer between systems adds turbulence. Filling steps and contact with packaging materials can introduce more air if controls are loose.
This creates several downstream risks:
- Oxidation and reduced shelf life: Oxygen reacts with active components used in dental products manufacturing, altering flavor and weakening performance.
- Filling accuracy problems: Air compresses inside the paste. Tubes may look full but fall short by weight, which causes complaints and compliance risks.
- Sealing failures: Air pockets near the tube opening interfere with sealing, leading to leaks during shipping or shelf display.
These risks apply across oral care categories, from children’s toothpaste to premium lines inspired by ancient remedies or benchmark brands like Crest toothpaste.
How Vacuum Emulsifying Technology Eliminates Air
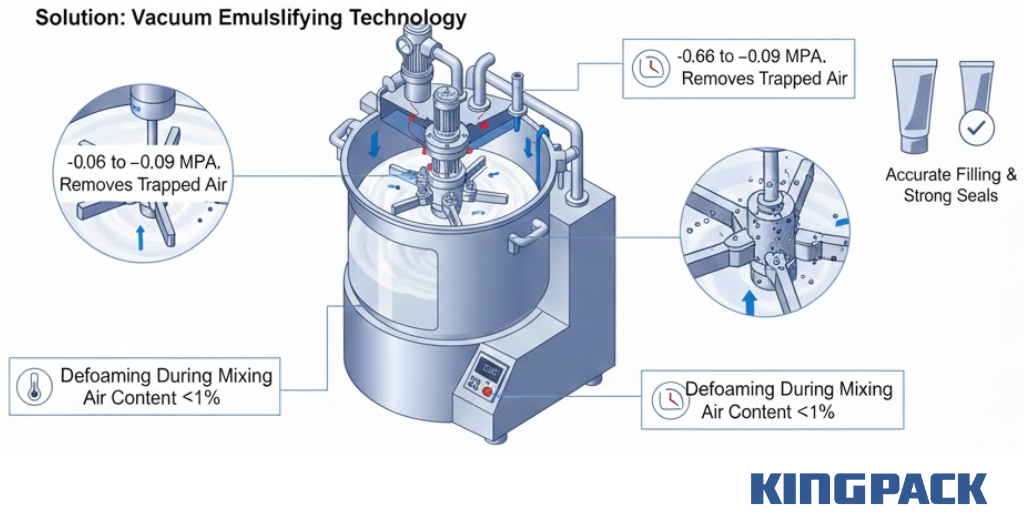
- Defoaming during mixing: Vacuum removes air during blending, lowering internal air content before filling.
- Accurate filling and sealing: Reduced air supports stable weight control and reliable tube closure.
- Oxidation control: Limiting oxygen exposure protects formula integrity from the start.
King Pack systems are built for high-viscosity pastes and stable output. Their solutions support contract manufacturer setups, private label lines, and advanced production units using industrial standards similar to BO International and Ginhong Mixers. This approach delivers uniform paste, reliable packaging flow through labeling machines, and consistent results aligned with package design and market expectations.
Challenge 3 – Hygiene Risks and GMP Compliance

Toothpaste contacts consumers directly, so hygiene is critical. Contamination with bacteria, mold, or foreign particles creates health risks and regulatory issues.
Hygiene Challenges in Traditional Lines:
- Equipment design: Dead spaces and rough surfaces trap residue and microbes.
- Manual transfers: Moving product between stations introduces contamination risk.
- Cleaning pressures: Limited downtime can lead to insufficient cleaning, while over-cleaning wastes resources.
Studies show consumers are 70% more likely to choose FDA-approved toothpaste, emphasizing the need for strict hygiene.
How Integrated GMP-Compliant Lines Help
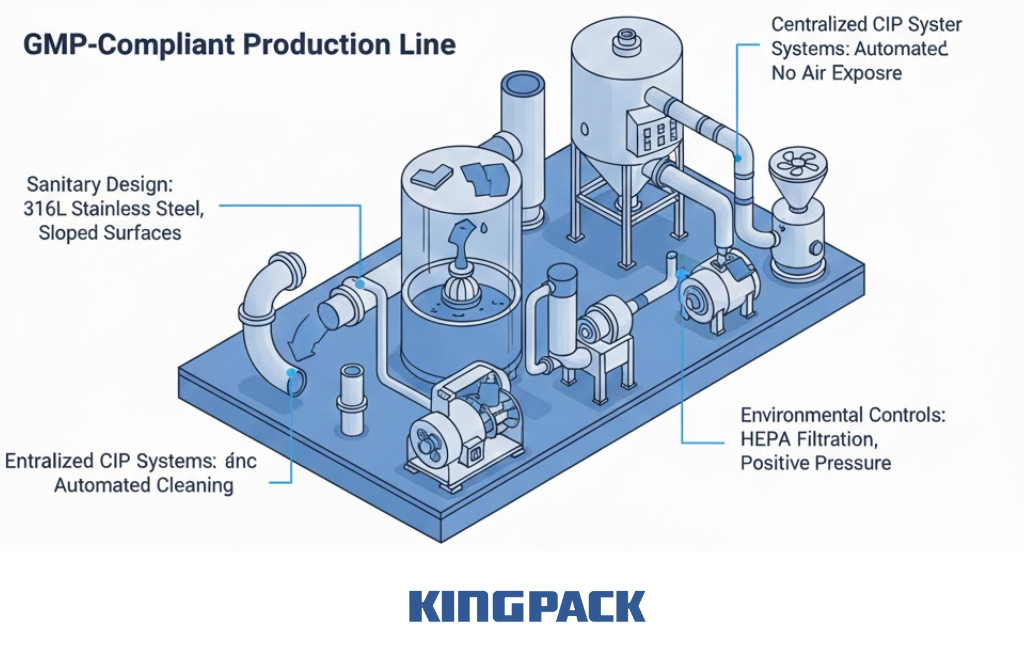
- Sanitary design: Stainless steel 316L, sloped surfaces, and tri-clamp fittings prevent residue buildup and simplify inspection.
- Centralized CIP systems: Automated cleaning flows through mixers, pipelines, and fillers, using pre-programmed washes with sensors verifying completeness.
- Enclosed transfer systems: Vacuum pipelines move paste without exposure to air, reducing contamination risks.
- Environmental controls: HVAC with HEPA filtration and positive pressure maintain clean processing conditions continuously.
King Pack’s integrated lines combine these features, ensuring consistent hygiene, regulatory compliance, and safe toothpaste production.
Challenge 4 – Filling Accuracy and Tube Sealing Quality
Dosing precision affects both profitability and regulatory compliance. Overfilling wastes product and reduces margins. Underfilling violates weight declarations and creates consumer dissatisfaction. Poor sealing leads to product leakage and shelf life problems.
Problems Caused by Inaccurate Filling
Manual and semi-automatic filling operations struggle with consistency. Operator variation affects dose amounts even with the best training. Fatigue during long production runs amplifies these variations.
Paste viscosity changes during production affect filling accuracy. As ambient temperature fluctuates, the paste becomes thicker or thinner. Manual filling systems cannot compensate for these rheological changes.
The financial impact compounds quickly. A 50,000 tube per day production line that consistently overfills by just 2% wastes approximately $50,000 in product annually. This waste directly impacts profitability without creating any consumer value.
Sealing defects create different but equally serious problems:
- Leakage during distribution: Improper seals allow paste to escape tubes during shipping. Retailers reject contaminated cartons, creating costly returns and damaging brand reputation.
- Reduced shelf life: Micro-gaps in seals allow air infiltration. Oxidation begins immediately, degrading product quality. Consumers experience off-flavors and color changes long before the printed expiration date.
- Regulatory non-compliance: Weight verification testing may fail if tubes lose product through faulty seals. This creates potential recall situations and regulatory penalties.
How Automatic Tube Filling & Sealing Solves This
Servo-driven filling systems achieve remarkable precision. These systems use closed-loop control that monitors actual dispensed volume. Corrections occur automatically if variations appear.
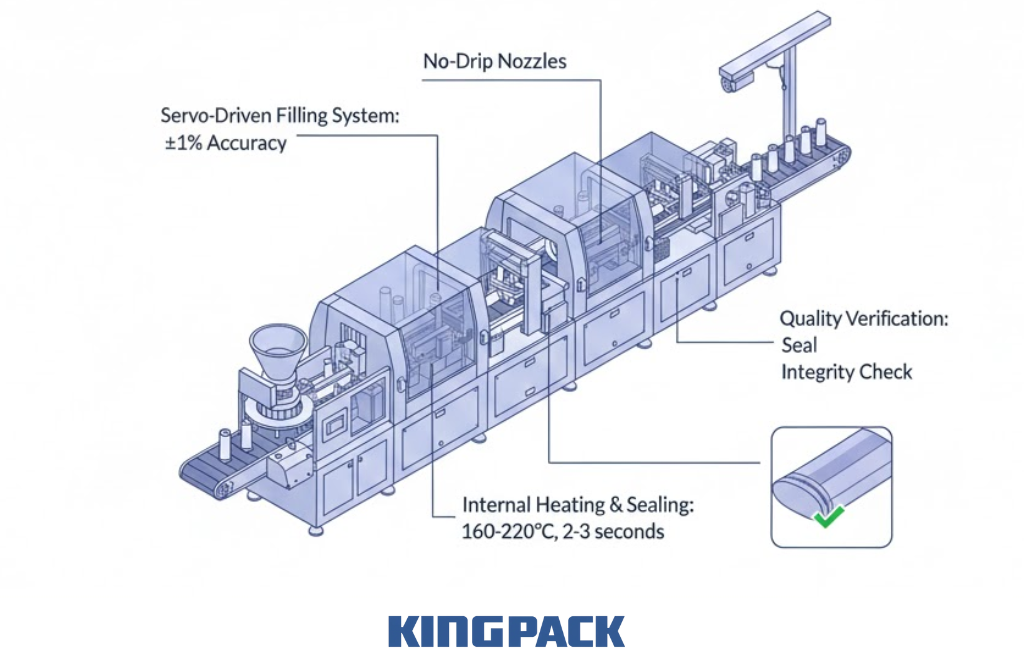
King Pack’s automatic tube filling and sealing machines maintain ±1% filling accuracy across production runs. This precision meets regulatory requirements while minimizing product waste. Servo motors provide exact dose control regardless of paste viscosity or temperature variations.
The filling process coordinates multiple operations:
- Tube feeding and orientation: Automatic loading systems position tubes correctly before filling. Vision systems inspect tubes and reject defective ones before paste enters the line.
- Precision dosing: Servo-driven pumps dispense exact amounts. No-drip nozzles prevent product waste and maintain cleanliness. Multiple filling stations increase throughput while maintaining individual dose accuracy.
- Internal heating and sealing: Sealed ends receive precise temperature application. Heating elements apply 160-220°C for 2-3 seconds depending on tube material. Pressure controls compress tube ends during heating for optimal seal formation.
- Quality verification: Integrated systems check seal integrity immediately after formation. Reject mechanisms remove any tubes with questionable seals before they reach packaging operations.
Automated sealing provides consistent results that manual operations cannot match. Temperature, pressure, and dwell time remain identical for every tube. This consistency creates reliable seals that protect product integrity throughout distribution and shelf life.
Recommended Reading: How Does a Tube Filling Machine Work? – King Pack Machinery
Challenge 5 – Low Efficiency and High Labor Costs
Labor is one of the largest cost drivers in toothpaste manufacturing. Manual and semi-automatic lines need operators at several stations, which limits speed and raises operating costs. Human-dependent processes also lose consistency over long shifts.
Common Bottlenecks in Conventional Lines

Traditional setups create recurring constraints:
- Manual tube loading: Operators feed tubes one by one. Line speed usually caps at 30–40 tubes per minute, with output dropping as fatigue sets in.
- Manual quality checks: Visual inspection of fill level and seal quality slows flow and creates queues at the filler discharge.
- Slow batch changeovers: Manual cleaning and mechanical adjustments can take 2–4 hours. Labor costs continue during downtime while production stops.
- Material handling delays: Transferring paste between mixers, storage tanks, and fillers requires extra staff and adds handling risk.
Industry data shows that automated systems can replace the workload of roughly 2.5 operators while delivering stable output across full shifts.
How Integrated Automatic Lines Improve Productivity
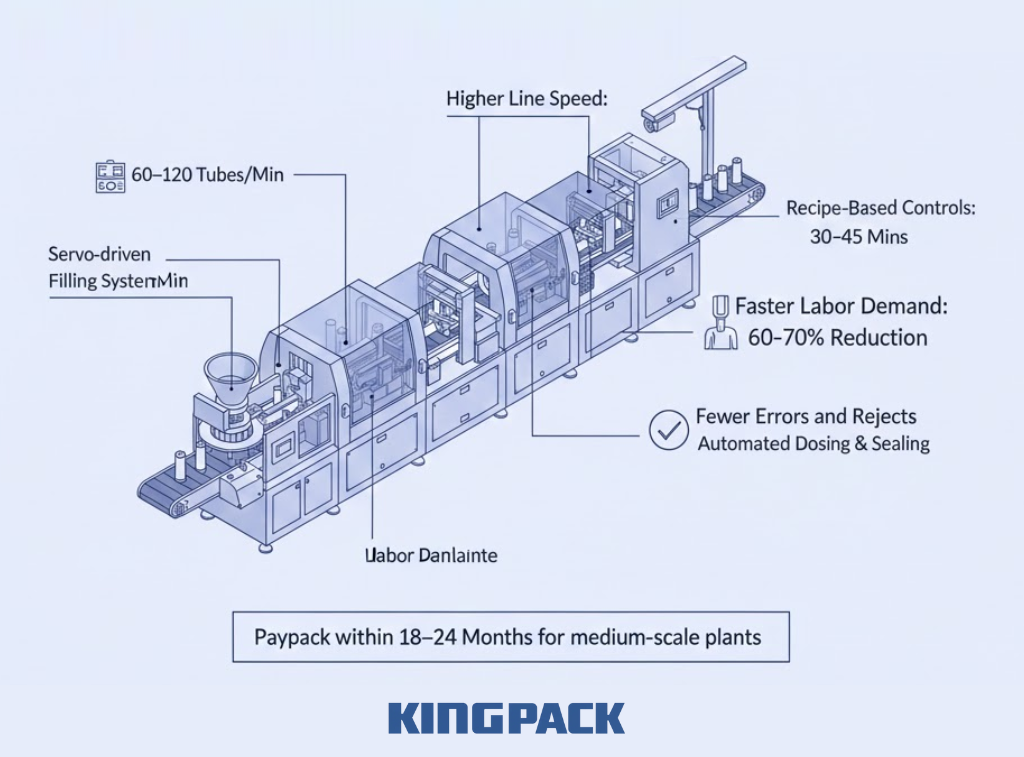
Fully integrated lines remove these bottlenecks by automating every stage from mixing to packaging.
Key productivity gains include:
- Higher line speed: Automatic filling and sealing systems run at 60–120 tubes per minute, doubling or tripling output.
- Lower labor demand: Direct labor needs typically drop by 60–70%. Staff shift from repetitive tasks to supervision and quality control.
- Faster changeovers: Recipe-based controls cut changeover time to about 30–45 minutes.
- Fewer errors and rejects: Automated dosing and sealing reduce waste and rework.
For medium-scale plants producing around 30,000 tubes per day, the combined impact of labor savings and higher output often delivers payback within 18–24 months.
What Is an Integrated Toothpaste Production Line?
An integrated toothpaste production line connects all manufacturing stages into one coordinated system. Instead of standalone machines with manual transfers, materials move automatically from raw ingredient handling to finished, packaged tubes.
This setup improves control and efficiency. Centralized PLC systems manage mixing, transfer, filling, and packaging from a single interface. Automated vacuum transfer eliminates manual handling, reducing contamination risk and product loss.
Equipment operates in sync, so filling speed matches mixer output and packaging keeps pace without bottlenecks. Cleaning also becomes simpler, since CIP cycles run across the entire line rather than on individual machines.
King Pack designs turnkey integrated systems that arrive pre-engineered and factory-tested, shortening installation and commissioning timelines.
Recommended Reading: What Machines Are Used to Make Toothpaste? – King Pack Machinery
Key Equipment in King Pack’s Integrated Toothpaste Line
Complete production lines combine specialized equipment optimized for toothpaste manufacturing.
1). Vacuum Emulsifying Mixer
This equipment forms the core of toothpaste production. Vacuum emulsifying mixers blend ingredients under negative pressure while applying high-shear homogenization.
KPYGP-500L Toothpaste machine – King Pack Machinery
Capacities range from 50L for pilot production to 2000L for commercial operations. Jacketed vessels provide heating and cooling. Multiple inlet ports allow controlled ingredient addition. CIP systems clean internal surfaces automatically.
King Pack’s mixers feature 316L stainless steel construction throughout. Variable frequency drives adjust mixing speeds for different formulations. Vacuum systems maintain consistent negative pressure during operation.
2). Aging & Storage Tanks
Post-mixing storage allows formulations to stabilize before filling. Aging tanks hold product for 24-72 hours while viscosity stabilizes and flavors mature.
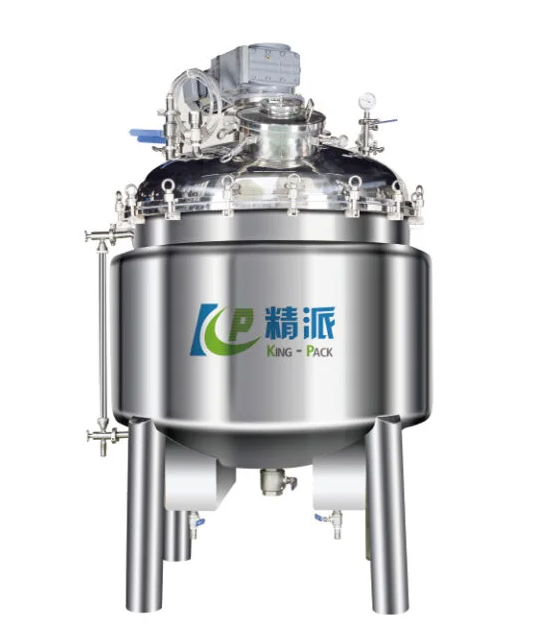

Agitator tank – King Pack Machinery
Gentle agitation prevents settling without introducing air. Jacketed tanks maintain temperature during storage. Sloped bottoms facilitate complete discharge. Sanitary fittings meet GMP requirements.
Tank sizing matches production schedules. Typical configurations include 2-3 storage tanks allowing continuous filling operations while new batches undergo mixing.
3. Transfer Pumps & Pipelines
Specialized pumps move viscous toothpaste between processing stages. Lobe pumps or progressive cavity pumps handle high-viscosity pastes without degrading product structure.
Sanitary pipelines use tri-clamp connections for easy disassembly. Electropolished internal surfaces minimize product adhesion. Sloped piping prevents product pooling. CIP systems clean pipelines between batches.
King Pack designs transfer systems with appropriate sizing for each formulation’s rheology. Proper pump selection prevents product damage during transfer.
4. Automatic Tube Filling and Sealing Machine
These machines combine multiple operations into integrated systems. Tubes load automatically, receive precise paste doses, seal with internal heating, and discharge for packaging.

KPGFW-160 Filling and sealing machine – King Pack Machinery
Servo-driven filling provides ±1% accuracy. Vision systems inspect tubes before and after filling. Reject mechanisms remove defective units. Coding systems print batch numbers and dates.
Stainless steel construction maintains hygiene. User-friendly controls simplify operation. Quick-change tooling accommodates different tube sizes.
5. Secondary Packaging Equipment
Automatic cartoning machines fold cartons, insert tubes, and seal boxes. These systems integrate with filling operations for complete automation.
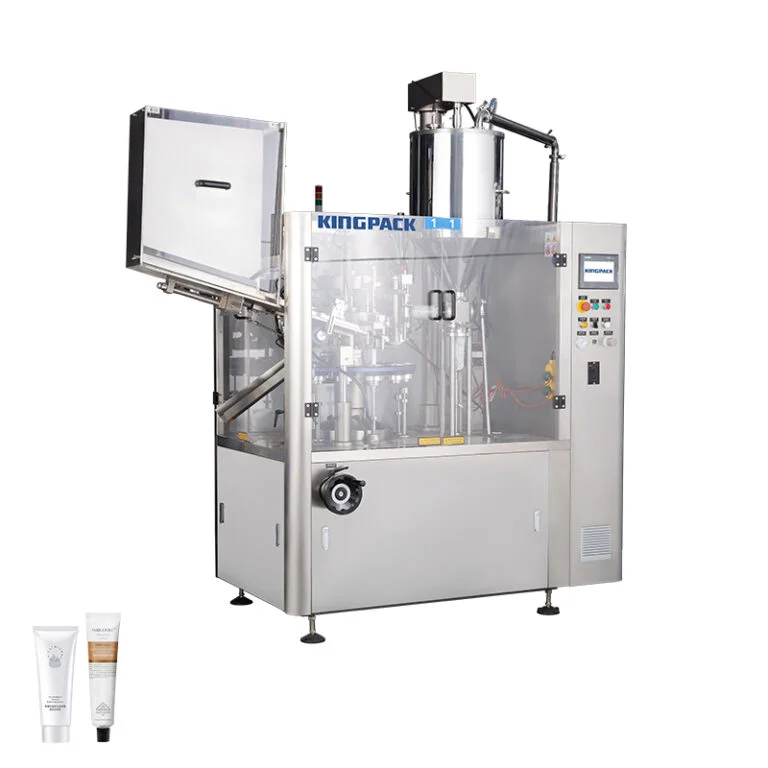

KPGFW-80 Fully Automatic Plastic & Aluminum Tube Filling and Sealing Machine – King Pack Machinery
Pick-and-place robots handle tubes gently while maintaining high speeds. Carton magazines hold blank boxes. Hot melt sealers close cartons securely. Optional case packing and palletizing extend automation through warehouse preparation.
Why King Pack Integrated Toothpaste Production Lines
King Pack designs integrated toothpaste lines with a focus on GMP-compliant construction, system-level engineering, and long-term operational reliability. Each line is built to maintain consistent product quality, improve efficiency, and reduce downtime across all production stages.
Single-source responsibility simplifies project management by providing one point of contact for design, installation, and commissioning. Custom layouts are tailored to your specific formulations, production capacity, and future expansion plans, ensuring that the line grows with your business needs.
Global installation and after-sales support ensure smooth operation from day one. King Pack’s teams handle equipment delivery, system integration, operator training, and ongoing technical support. Regular maintenance programs, remote diagnostics, and spare parts supply keep production consistent and minimize unplanned downtime.
By combining engineering expertise, turnkey solutions, and full lifecycle support, King Pack enables manufacturers to run high-quality, efficient, and scalable toothpaste production lines with confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What production capacities are supported?
Integrated lines handle 5,000 to over 100,000 tubes per day. Capacity depends on tube size, paste viscosity, and automation level, and can be customized for future growth.
2. Can one line handle multiple formulations?
Yes. Vacuum emulsifying mixers and servo-driven filling systems accommodate a wide viscosity range. Operators can switch between recipes without mechanical adjustments when parameters are within validated limits.
3. Can existing lines be upgraded?
Often, semi-automatic lines can be upgraded to full integration. Options include automated tube feeding, CIP systems, and integrated filling and sealing modules with minimal downtime.
4. How is cleaning handled?
Centralized CIP circuits clean mixers, tanks, pumps, and pipelines in a single cycle. This ensures consistent hygiene while saving time compared to manual or separate cleaning methods.
5. What is the project timeline?
Standard equipment delivery takes 10–16 weeks depending on customization. Installation and commissioning add 3–5 weeks, with operator training completed during startup.
Conclusion
Integrated toothpaste production lines improve quality, hygiene, and throughput by controlling the process from mixing to final packaging. With the right system design, manufacturers reduce waste, stabilize filling performance, and scale production with confidence.
To plan a fully integrated toothpaste production line or upgrade an existing facility, contact King Pack Filling for technical consultation and tailored system design.

